
Introduction
Loneliness is a powerful emotional state that can impact various aspects of a person’s life, including mental health and behavior. One of the most concerning effects of chronic loneliness is its connection to substance abuse. For many individuals, the pain of feeling disconnected and isolated can drive them to seek comfort in drugs or alcohol. Unfortunately, this coping mechanism can quickly spiral into a vicious cycle where loneliness fuels substance abuse, and substance abuse exacerbates loneliness. In this post, we will explore the relationship between loneliness and substance abuse, how they reinforce each other, and the steps that can be taken to break the cycle.
The Link Between Loneliness and Substance Abuse
1. Loneliness as a Trigger for Substance Abuse
Loneliness can create deep emotional pain, which some individuals attempt to numb through the use of substances. Whether it’s alcohol, drugs, or even prescription medication, the temporary escape provided by substances can offer a momentary sense of relief from the emotional weight of isolation. People who feel disconnected from others may be more likely to turn to these substances to manage their feelings of sadness, anxiety, or despair. Over time, however, the use of substances can become a habit or coping mechanism, leading to addiction.
2. Substance Abuse as a Means of Escaping Negative Emotions
Substance abuse often serves as a way for individuals to escape the negative emotions associated with loneliness, such as sadness, hopelessness, or self-worth issues. These emotional struggles can intensify when a person feels they have no one to turn to for support or understanding. The temporary high provided by substances may help alleviate emotional pain in the short term, but this relief is short-lived, leaving individuals feeling worse once the effects wear off. This creates a cycle where the person feels compelled to use substances again to cope with the loneliness, reinforcing the behavior.
3. Social Isolation and Substance Dependency
Over time, substance abuse can lead to increased social isolation. Individuals who become dependent on drugs or alcohol often withdraw from social interactions, either because of shame, guilt, or the effects of their addiction. As their social circle shrinks, they may experience even greater feelings of loneliness. This isolation further feeds the need for substance use, creating a self-perpetuating cycle of loneliness and addiction.
How Loneliness Exacerbates the Impact of Substance Abuse
1. Decreased Emotional Support
When individuals experience loneliness, they often lack the emotional support system needed to recover from or manage their substance abuse. Social support plays a critical role in addiction recovery by providing encouragement, accountability, and understanding. Without this support, individuals may find it difficult to break free from their addiction, making it harder to maintain sobriety. The absence of close relationships makes it easy to fall back into old habits when faced with stress or difficult emotions.
2. Emotional and Psychological Deterioration
Chronic loneliness can lead to severe emotional and psychological deterioration, including depression and anxiety, both of which are commonly linked to substance abuse. When someone feels isolated, they may experience a decline in self-esteem, feelings of worthlessness, and a sense of hopelessness. These negative emotions can contribute to an increased desire to numb the pain through alcohol or drugs. As substance abuse continues, the emotional and psychological health of the individual continues to decline, deepening both their loneliness and their dependence on substances.
3. Escalation of Substance Use
The relationship between loneliness and substance abuse often leads to an escalation in substance use. As an individual’s loneliness persists and deepens, they may begin using larger quantities of substances or using them more frequently in an attempt to escape their emotions. Over time, this can lead to physical dependence and addiction, which only intensifies feelings of isolation and despair. The longer the cycle continues, the harder it becomes to break free from the grips of both loneliness and addiction.
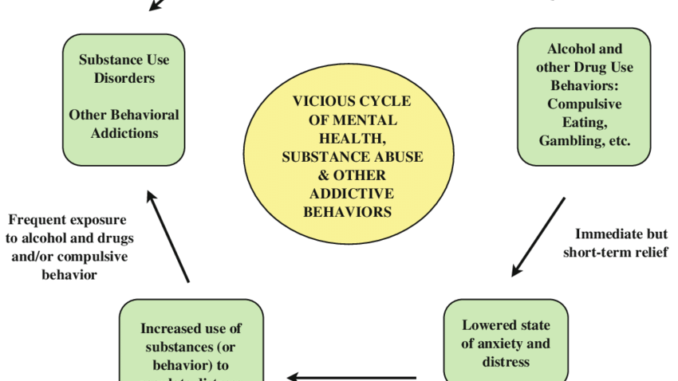
The Cycle of Loneliness and Substance Abuse: A Vicious Loop
The cycle of loneliness and substance abuse becomes vicious because each aspect amplifies the other. As loneliness drives individuals to seek comfort in substances, the subsequent substance abuse leads to more social isolation and emotional pain, reinforcing the desire to use again. This cycle can be incredibly difficult to break without professional intervention and support. Let’s look at how this loop unfolds:
- Loneliness triggers emotional pain →
- Substance abuse is used as a coping mechanism →
- Substance abuse leads to social isolation →
- Isolation intensifies feelings of loneliness →
- Loneliness increases emotional pain →
- The cycle repeats with escalating substance use.
The longer this cycle continues, the harder it becomes to break. People often feel trapped in this loop, unable to see a way out without help.
Breaking the Cycle: How to Overcome Loneliness and Substance Abuse
1. Building Social Connections
One of the most effective ways to break the cycle of loneliness and substance abuse is to build or rebuild meaningful social connections. Engaging in group therapy, support groups, or community activities can provide individuals with the emotional support they need to confront their loneliness. Reaching out to friends and family members or joining a social network that promotes positive interactions can help reduce feelings of isolation.
2. Seeking Professional Help
Professional treatment is often necessary to address both loneliness and substance abuse. Therapy, whether it’s cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), counseling, or addiction treatment, can help individuals address the root causes of their loneliness and teach healthier coping mechanisms. Detox programs and rehabilitation centers also provide individuals with the resources needed to recover from addiction while simultaneously offering support for mental and emotional challenges.
3. Developing Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Instead of turning to substances to cope with loneliness, individuals can learn healthier coping strategies. Practices like mindfulness, meditation, physical activity, and journaling can help individuals manage negative emotions without relying on substances. These activities promote mental well-being, reduce stress, and increase feelings of self-worth. Additionally, spending time outdoors or engaging in creative hobbies can help foster a sense of connection with oneself and others.
4. Establishing a Routine and Purpose
A structured routine and a sense of purpose can help individuals manage loneliness and avoid the temptation of substance abuse. Setting daily goals, pursuing hobbies, or finding meaningful work can provide a sense of accomplishment and reduce idle time, which may otherwise lead to substance use. Purpose-driven activities, such as volunteering or helping others, can foster a sense of connection and reduce feelings of isolation.
Conclusion
The connection between loneliness and substance abuse is complex and deeply rooted in emotional, psychological, and social factors. Loneliness often serves as both a trigger and a consequence of substance abuse, creating a vicious cycle that is difficult to break. However, by addressing the underlying causes of loneliness, seeking professional help, and developing healthier coping strategies, individuals can start to dismantle this cycle. Breaking free from the grip of loneliness and addiction is possible with the right support and resources. By fostering meaningful connections, adopting healthier habits, and seeking treatment, individuals can work towards long-term recovery and a more fulfilling, connected life.

Leave a Reply