
Healthcare outcomes are not only shaped by medical interventions but also by a complex array of social factors. These factors, known as social determinants of health (SDOH), include conditions in the environment where people are born, live, learn, work, play, and age. They have a profound effect on individuals’ health and well-being, influencing how people access healthcare services, manage their health, and respond to treatments. This article explores the impact of social determinants of health on healthcare outcomes, shedding light on how these factors shape health disparities and highlighting the need for comprehensive healthcare strategies that address these social issues.
What Are Social Determinants of Health?
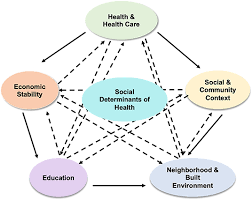
Social determinants of health refer to the non-medical factors that influence health outcomes. These factors can have a significant impact on an individual’s ability to maintain good health and access healthcare services. Some of the most critical social determinants include:
- Economic Stability: Income, employment status, and financial security
- Education: Educational attainment, literacy, and language skills
- Social and Community Context: Social relationships, community engagement, and support networks
- Health Care Access and Quality: Access to medical services, health insurance, and quality of care
- Neighborhood and Built Environment: Housing conditions, transportation, access to healthy food, and safety in communities
These factors interact in complex ways and contribute to disparities in healthcare access and health outcomes across different populations.
How Social Determinants Influence Healthcare Outcomes
Social determinants of health play a major role in shaping both the physical and mental health of individuals. Let’s explore how these determinants affect healthcare outcomes:
1. Economic Stability and Access to Healthcare
Economic factors, such as income level and employment status, directly affect access to healthcare. People with lower incomes often face challenges in accessing quality healthcare services due to the inability to afford insurance, high out-of-pocket costs, or lack of access to healthcare providers in their area.
Individuals living in poverty are also more likely to experience chronic stress, which can lead to poor health outcomes like hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease. The lack of financial resources can limit their ability to engage in preventive care, leading to more serious health issues later on.
2. Education and Health Literacy
Education plays a critical role in shaping health outcomes. People with higher levels of education are more likely to make informed decisions about their health, adhere to medical advice, and seek appropriate healthcare services when needed. Conversely, individuals with lower education levels may struggle with health literacy, making it more difficult for them to understand medical instructions, navigate the healthcare system, or engage in preventive care.
Health literacy also affects how well individuals can manage chronic conditions. For example, a person with limited health literacy might have trouble understanding how to properly take medications or follow a treatment plan, leading to poorer health outcomes.
3. Social and Community Context
Strong social relationships and community engagement have a positive impact on health. People with strong family and social support networks are better equipped to handle stress, manage chronic illnesses, and recover from health setbacks. Social isolation, on the other hand, can lead to increased risk of mental health issues, substance abuse, and chronic conditions like heart disease.
Living in supportive communities can also provide access to resources like safe recreational spaces, community health programs, and wellness support groups, all of which promote better health outcomes.
4. Healthcare Access and Quality
Access to quality healthcare services is a fundamental social determinant of health. In many communities, particularly in rural or low-income urban areas, healthcare access can be limited due to factors like geographic location, lack of transportation, or scarcity of healthcare providers. This often leads to delays in diagnosis, lack of preventive care, and insufficient treatment for chronic conditions.
Additionally, health disparities exist based on race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. Minority and marginalized groups may face discrimination or bias in healthcare settings, resulting in poorer care and negative health outcomes. Ensuring equal access to quality healthcare for all populations is critical in addressing these disparities.
5. Neighborhood and Built Environment
The physical environment where people live can greatly influence their health. Poor housing conditions, inadequate sanitation, and exposure to environmental hazards like pollution can contribute to a wide range of health problems, including respiratory diseases, infections, and mental health issues.
Access to healthy food is another key factor. People living in “food deserts,” or areas with limited access to fresh and nutritious food, often struggle to maintain a healthy diet. This can lead to obesity, diabetes, and other diet-related diseases. Additionally, the safety of neighborhoods and the availability of public transportation can impact people’s ability to access healthcare and engage in physical activity, further influencing their health.
Health Disparities: The Role of Social Determinants
Social determinants of health are a major driver of health disparities—differences in health outcomes that are closely linked with social, economic, and environmental factors. These disparities disproportionately affect vulnerable populations, including racial and ethnic minorities, low-income individuals, and people living in rural areas.
For example, research has shown that African American, Latino, and Native American populations experience higher rates of chronic diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, and obesity compared to their white counterparts. These disparities are often exacerbated by systemic barriers, including limited access to quality healthcare, lower levels of education, and economic instability.
Addressing these disparities requires a multifaceted approach that involves not only improving healthcare access but also tackling the underlying social determinants that contribute to unequal health outcomes.
Addressing Social Determinants: A Comprehensive Approach
To reduce health disparities and improve healthcare outcomes, it is essential to address the root causes of social determinants. Here are some strategies that can help tackle these issues:
1. Improving Access to Healthcare
Efforts to expand access to healthcare, such as through Medicaid expansion or increasing the availability of affordable health insurance plans, can help individuals from all socioeconomic backgrounds receive the care they need. Providing access to primary care services, preventative health programs, and mental health services is crucial in reducing the burden of chronic diseases.
2. Investing in Education and Health Literacy
Improving education systems and increasing access to health literacy programs can empower individuals to take control of their health. Health education campaigns can also help raise awareness about preventive care, healthy lifestyles, and the importance of seeking medical advice.
3. Building Stronger Social Support Networks
Community-building efforts can help reduce social isolation and foster stronger support systems. This can include creating community health programs, providing family support services, and enhancing social engagement opportunities for people in underserved areas.
4. Addressing Environmental and Housing Issues
Improving the built environment through better housing, safer streets, and access to clean air and water can significantly impact public health. Community-based initiatives that focus on improving neighborhoods, creating walkable spaces, and increasing access to healthy food can help mitigate the effects of negative environmental determinants.
5. Policy Changes and Advocacy
Policymakers play a crucial role in addressing social determinants of health. By advocating for policies that promote equitable healthcare access, reduce poverty, and improve education and employment opportunities, society can create an environment where everyone has the opportunity to lead a healthy life. Addressing systemic racism and discrimination in healthcare systems is also an essential part of this work.
Conclusion
Social determinants of health are central to understanding healthcare outcomes and addressing health disparities. Economic stability, education, access to healthcare, social support, and the environment all contribute to an individual’s overall health. By recognizing the impact of these factors, we can develop more effective, equitable healthcare policies and strategies that aim to improve health outcomes for everyone, regardless of their background or circumstances.
Efforts to address social determinants of health must be comprehensive and multifaceted, combining healthcare improvements with community support, education, and systemic policy changes. Only by addressing these broader social factors can we create a healthier, more equitable society where everyone has the opportunity to thrive.

Leave a Reply