
Healthcare inequality remains a pressing issue across the globe, affecting millions of individuals, especially in underserved communities. From lack of access to essential care to discrepancies in treatment quality, healthcare inequality has profound implications for both individuals and entire populations. Bridging the healthcare gap is crucial to ensure everyone, regardless of their socioeconomic status, location, or background, can access the care they need. This article explores the causes, impact, and potential solutions for healthcare inequality, with a focus on creating a more equitable healthcare system.
What is Healthcare Inequality?
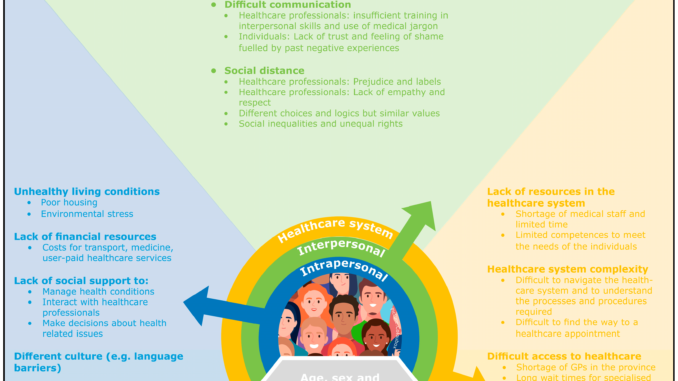
Healthcare inequality refers to the disparities in access to, quality of, and outcomes from healthcare services. These disparities are often driven by a range of factors, including socioeconomic status, geographic location, race, gender, and disability status. Healthcare inequality can manifest in various ways, such as unequal access to medical services, differences in treatment outcomes, and disparities in healthcare coverage.
At its core, healthcare inequality leads to significant gaps in health outcomes, with marginalized populations experiencing poorer health and shorter life expectancy. Understanding these inequalities is crucial for finding effective solutions and ensuring better healthcare for all.
Causes of Healthcare Inequality
Several factors contribute to healthcare inequality. These causes can be broadly categorized into economic, social, and systemic issues.
1. Socioeconomic Status
Individuals from lower-income backgrounds often face significant barriers to accessing quality healthcare. These barriers may include inability to afford insurance, high out-of-pocket costs for medical treatments, and limited access to medical providers. People with lower socioeconomic status are more likely to experience poor health outcomes due to these financial constraints.
2. Geographic Location
Rural and remote areas often face unique healthcare challenges. In these regions, there may be a lack of healthcare infrastructure, fewer medical professionals, and limited access to specialized care. This can result in delayed diagnoses, inadequate treatment, and higher rates of preventable conditions.
3. Racial and Ethnic Disparities
Racial and ethnic minorities often experience poorer health outcomes compared to their white counterparts. This is partly due to systemic racism within the healthcare system, where patients from minority groups may face discrimination, implicit bias from healthcare providers, and barriers to care. These disparities can lead to misdiagnosis, delayed treatment, and overall worse health outcomes.
4. Gender and Sexual Orientation
Gender inequality in healthcare can manifest in several ways. Women may face challenges in receiving equitable care, particularly for reproductive health. LGBTQ+ individuals may also encounter discrimination or lack of understanding regarding their specific healthcare needs. These challenges can prevent individuals from seeking care and receiving the treatment they deserve.
5. Disability and Chronic Conditions
People with disabilities and chronic conditions often face significant barriers to accessing adequate healthcare. These barriers may include physical accessibility issues, lack of proper accommodations, and healthcare professionals’ lack of training in treating individuals with disabilities. In addition, people with chronic conditions may experience long wait times for appointments and inadequate management of their conditions.
Impact of Healthcare Inequality
Healthcare inequality has far-reaching consequences that go beyond individual patients. These disparities contribute to larger public health issues and strain healthcare systems. Some of the key impacts include:
1. Worsening Health Outcomes
Inequality in healthcare access leads to delayed diagnoses, missed treatments, and higher mortality rates, particularly for preventable conditions. For example, individuals without adequate healthcare access are less likely to receive timely screenings for conditions like cancer or heart disease, which can result in more advanced stages of illness when diagnosed.
2. Increased Healthcare Costs
Inequality in healthcare results in greater long-term costs for both individuals and the healthcare system as a whole. When individuals lack access to primary care and preventive services, they are more likely to seek emergency care, which is more expensive and less effective in the long run. These higher costs contribute to the overall inefficiency of the healthcare system.
3. Mental Health Implications
Healthcare inequality also affects mental health. Individuals facing barriers to accessing care may experience increased stress, anxiety, and depression due to their inability to address physical health needs. This compounded mental health burden can further exacerbate health inequalities, creating a cycle of poor health outcomes.
4. Social and Economic Inequities
The broader social and economic impact of healthcare inequality is also significant. Poor health can prevent individuals from working, attending school, or participating fully in society. This perpetuates the cycle of poverty, as individuals who lack access to healthcare are often unable to improve their economic status.
Bridging the Gap: Solutions for Healthcare Inequality
Addressing healthcare inequality requires a multi-faceted approach that includes policy changes, community-based solutions, and structural improvements within the healthcare system. Here are some potential solutions to help bridge the gap and create a more equitable healthcare environment:
1. Expanding Access to Care
Increasing access to healthcare services is one of the most effective ways to address inequality. Expanding Medicaid, implementing universal health coverage, and creating more affordable insurance options can help ensure that more people, regardless of income, can access the care they need. Additionally, increasing funding for healthcare infrastructure in rural and underserved areas can improve access for those living in remote locations.
2. Reducing Healthcare Costs
Efforts to reduce the cost of healthcare services are essential to ensuring that people from all socioeconomic backgrounds can afford care. This can include measures such as price transparency, negotiating lower drug costs, and reducing out-of-pocket expenses for essential healthcare services. These steps would make it easier for individuals to seek preventive care and avoid expensive emergency treatments.
3. Improving Health Literacy
Health literacy plays a critical role in preventing healthcare disparities. People who do not understand how to navigate the healthcare system or manage their health are at greater risk of poor health outcomes. Programs that promote health education and literacy can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and seek care when needed.
4. Addressing Systemic Racism
Healthcare systems must take steps to address systemic racism and implicit bias within their practices. This includes better training for healthcare providers on cultural competence, implementing policies that promote diversity and inclusion, and creating mechanisms for patients to report discrimination. Fostering an inclusive and respectful healthcare environment can improve trust and lead to better outcomes for marginalized communities.
5. Telemedicine and Digital Health
Telemedicine has proven to be a valuable tool in bridging the gap in healthcare access, particularly for individuals in rural areas. By using technology, patients can access care remotely, reducing the need for long travel times and increasing convenience. Expanding access to telehealth services can help improve healthcare access for underserved populations and reduce barriers to care.
6. Community-Based Healthcare Initiatives
Community-based healthcare models can provide more equitable access to care by meeting people where they are. Mobile clinics, local health centers, and outreach programs can help deliver essential services to communities that may not have access to traditional healthcare facilities. These initiatives can provide primary care, mental health support, and preventive services directly within underserved communities.
Conclusion
Healthcare inequality remains one of the most significant challenges in modern healthcare systems. The disparities in access, quality, and outcomes affect millions of individuals worldwide, particularly those from marginalized communities. Bridging the healthcare gap requires comprehensive solutions, including expanding access, reducing costs, addressing systemic biases, and leveraging technology.
By implementing these solutions, we can work toward creating a healthcare system that ensures equal access to high-quality care for all, regardless of background or socioeconomic status. Tackling healthcare inequality is not only a moral imperative but also a public health necessity that will improve the well-being of entire populations and contribute to a more just and equitable society.

Leave a Reply